-
its a basic question on how to calculate tax using python
over 9 years ago
-
over 9 years ago
Hi Auralia Malik, you can use the packages tax-calculation 0.6.8 in your python code library. then you can find the calculation of taxes as per country and as per state. Below i have done this code in cloud-tax calculation-:
import copy import numpy as np import taxcalc 0.6.8 from .utils import * from .functions import * from .policy import Policy from .records import Records from .behavior import Behavior from .growth import Growth from .consumption import Consumption # import pdb class Calculator(object): """ Constructor for the Calculator class. Parameters ---------- policy: Policy class object this argument must be specified IMPORTANT NOTE: never pass the same Policy object to more than one Calculator. In other words, when specifying more than one Calculator object, do this: pol1 = Policy() rec1 = Records() calc1 = Calculator(policy=pol1, records=rec1) pol2 = Policy() rec2 = Records() calc2 = Calculator(policy=pol2, records=rec2) records: Records class object this argument must be specified IMPORTANT NOTE: never pass the same Records object to more than one Calculator. In other words, when specifying more than one Calculator object, do this: pol1 = Policy() rec1 = Records() calc1 = Calculator(policy=pol1, records=rec1) pol2 = Policy() rec2 = Records() calc2 = Calculator(policy=pol2, records=rec2) verbose: boolean specifies whether or not to write to stdout data-loaded and data-extrapolated progress reports; default value is true. sync_years: boolean specifies whether or not to syncronize policy year and records year; default value is true. behavior: Behavior class object specifies behaviorial responses used by Calculator; default is None, which implies no behavioral responses. growth: Growth class object specifies economic growth assumptions used by Calculator; default is None, which implies use of standard economic growth assumptions. consumption: Consumption class object specifies consumption response assumptions used to calculate "effective" marginal tax rates; default is None, which implies no consumption responses. Raises ------ ValueError: if parameters are not the appropriate type. Returns ------- class instance: Calculator """ def __init__(self, policy=None, records=None, verbose=True, sync_years=True, behavior=None, growth=None, consumption=None): if isinstance(policy, Policy): self._policy = policy else: raise ValueError('must specify policy as a Policy object') if isinstance(records, Records): self._records = records else: raise ValueError('must specify records as a Records object') if behavior is None: self.behavior = Behavior(start_year=policy.start_year) elif isinstance(behavior, Behavior): self.behavior = behavior else: raise ValueError('behavior must be None or Behavior object') if growth is None: self.growth = Growth(start_year=policy.start_year) elif isinstance(growth, Growth): self.growth = growth else: raise ValueError('growth must be None or Growth object') if consumption is None: self.consumption = Consumption(start_year=policy.start_year) elif isinstance(consumption, Consumption): self.consumption = consumption else: raise ValueError('consumption must be None or Consumption object') if sync_years and self._records.current_year == Records.PUF_YEAR: if verbose: print('You loaded data for ' + str(self._records.current_year) + '.') while self._records.current_year
-
over 9 years ago
If you are calculate this type tax then you easily manage the tax. and divide tax into many part as par your requirement.
Following these step given below
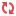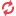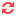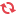
1- First we go to account module account -> configuration -> accounting ->Taxes and create tax as given below screen shoot
2- If you developer then you manage and chage account_tax function in .py file in
account module. -




2 Answer(s)