Conversion Operators are helpful in transforming the type of the item in a collection.
In linq, We have a three types of conversion operators:-
1. As operators(AsEnumerable and AsQueryable)
2. To operators(ToArray, ToDictionary, ToList and ToLookUp)
3. Casting operators(Cast and OfType)
1. As operators(AsEnumerable and AsQueryable)
These AsEnumerable and AsQueryable methods transform a input data to IEnumerable<T> or IQueryable<T>.
Example:-
class SampleProgram
{
static void ReportProperties<T>(T obj)
{
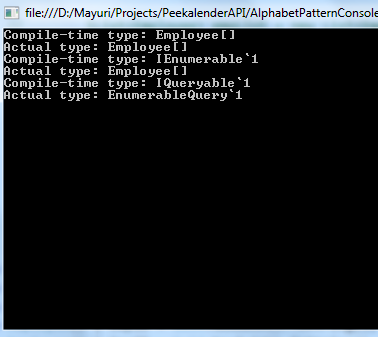
Console.WriteLine("Compile-time type: {0}", typeof(T).Name);
Console.WriteLine("Actual type: {0}", obj.GetType().Name);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Employee[] empArray = {
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "John", Age = 18 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Stefen", Age = 21 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Rami" , Age = 20 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Rohan" , Age = 31 }
};
ReportProperties( empArray );
ReportProperties(empArray.AsEnumerable());
ReportProperties(empArray.AsQueryable());
}
}
Output:-
2. To Operators(ToArray(), ToList(), ToDictionary())
These operators cast the input data to their corresponding type such as an Array, List or Dictionary respectively.
Example:-
Code:-
IList<int> numberList = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 30 ,14, 17};
int[] numArray = numberList.ToArray<int>();
IList<int> numList = numArray.ToList<int>();
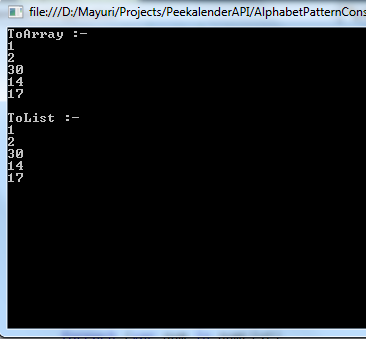
Console.WriteLine("ToArray :-");
foreach(var num in numberList )
{
Console.WriteLine(num);
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("ToList :-");
foreach(var num in numList)
{
Console.WriteLine(num);
}
Output:-
ToDictionary:- It is converts a generic list to a generic dictionary
Example:-
Code:-
IList<Employee> empList = new List<Employee>() {
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "John", Age = 18 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Stefen", Age = 21 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Rami" , Age = 20 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Rohan" , Age = 31 }
};
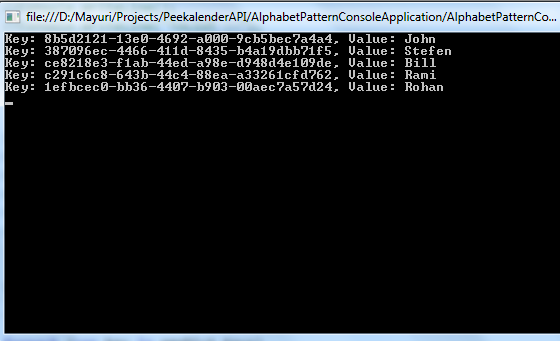
IDictionary<int, Employee> empDict =
empList.ToDictionary<Employee, int>(e => e.EmpID);
foreach(var key in empDict.Keys)
Console.WriteLine("Key: {0}, Value: {1}",
key, (empDict[key] as Employee).EmpName);
Output:-
3. Casting operators(Cast and OfType)
Cast:- Cast operator is used to convert a non-generic collection to a generic collection i.e. it convert a input data collection to the IEnumerable<T>.
Example:-
Code:-
class Program
{
static void ReportProperties<T>(T obj)
{
Console.WriteLine("Compile-time type: {0}", typeof(T).Name);
Console.WriteLine("Actual type: {0}", obj.GetType().Name);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Employee[] empArray = {
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "John", Age = 18 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Stefen", Age = 21 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Rami" , Age = 20 } ,
new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Rohan" , Age = 31 }
};
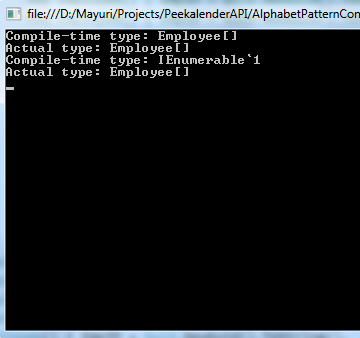
ReportProperties( empArray );
ReportProperties(empArray.Cast<Employee>());
}
}
Output:-
OfType:- It is used to filters a collection based on a specified type
Example:-
Code:-
IList list = new ArrayList();
list.Add(0);
list.Add("Zero");
list.Add(new Employee() { EmpID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), EmpName = "Stefen", Age = 21 });
var intResult = from l in list.OfType<string>() select l;
foreach(var item in intResult)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Output:-

0 Comment(s)